Gorgany Nature Reserve, Nadvirna
"Gorgany is a nature reserve located in Nadvirna district of Ivano-Frankivsk region. In administrative and economic terms, the territory of the reserve is divided into two nature conservation research departments - Gorgany and Chernyky. Area: 5344.2 hectares, with a surrounding protection zone of 3713.6 hectares. Subordination: Ministry of Ecology and Natural Resources of Ukraine
Visiting the territory for tourist purposes is prohibited. Only scientists may visit the territory with the permission of the administration and accompanied by the reserve's employees.
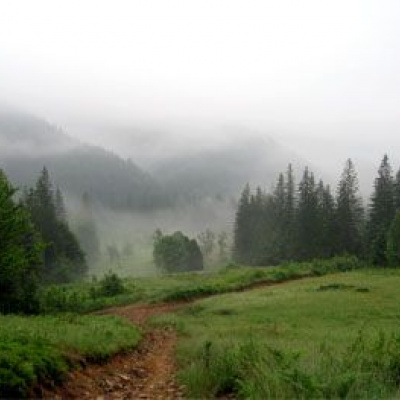
The Gorgany Nature Reserve is a natural benchmark of the central part of the Ukrainian Carpathians untouched by human activity and contains the only virgin forest of the Early Holocene relict - European pine in Europe and the world. It covers three climatic zones and five vertical stages of virgin, relict and endemic vegetation, habitats and wildlife populations in a continuous massif. The reserve contains a single continuous horizontal and vertical strip of five virgin forest subformations and demonstrates the stages of development of primary vegetation since the early Holocene. The rocky placers are home to some of the most stable post-glacial settlements of relict pine (Pinus sylvestris) and dark birch (Betula obscura). The largest centers of relict dendroflora and bedrock outcrops are known in the Gorgany, which are of scientific importance for studying the history of vegetation development in the postglacial period, and for researching dynamic trends in mountain and alpine ecosystems due to changing climatic conditions.
The first reserve of European cedar pine (formerly called cedar) in the Ukrainian Carpathians was established in the upper Limnytsia River near the village of Yasen in 1919. It covered an area of 178 hectares and was called "Gorgany". Later, another 2589 hectares were added to it. In 1935, also in the Limnytsia River basin, in the Yaytse tract, a 255.19-hectare Cedar Reserve was established on the lands of the Greek Catholic Church, and two years later, in the vicinity of Mount Hrofa, the Ukrainian Nature Park was established on an area of 1800 hectares.
In the basin of the Bystrytsia Nadvirna River, where the Gorgany Nature Reserve now operates, the Tavpyshyrka cedar reserve was established in the 1930s, covering an area of 583.85 hectares, which is now called the Tavpyshyrkivskyi State Reserve and is part of the Bystrytske Forestry of the Nadvirna Forestry State Enterprise.
In 1940, the government of the Ukrainian SSR issued a decree "On the organization of the Horhany State Reserve" (50 thousand hectares), which was never fully organized due to the outbreak of World War II. In the 50s and 80s of the twentieth century, a number of nature reserves, natural monuments, and protected tracts were created on the territory of the Nadvirna Timber Plant. In 1974, at the suggestion of Yurii Yurkevych, the Gorgan Reserve Forestry was organized. From 1946, Yurii Yurkevych worked as a senior forester at the Nadvirna Forestry, and after the reorganization of forestry, forestry and woodworking industry in 1959, until his retirement in 1971, he was the deputy director of forestry at the Nadvirna Timber Mill.
The Gorgany Nature Reserve was established by Presidential Decree No. 831/96 of September 12, 1996, covering an area of 5344.2 hectares. Its territory includes the Dzhurdzhi and Sadky landscape reserves of national importance, as well as the Chernyk, Hnyliak, Novobudova, Elmy, Dovzhynets, and Stoly protected tracts.
The Ivano-Frankivsk Regional State Administration's order of February 3, 1997, allocated a 750-1100-meter wide perimeter protection zone for five forestries bordering the reserve. The greatest efforts were made to create the reserve: Yurii Yurkevych, P.A. Trybun, K.K. Smagliuk, M.V. Cherniavskyi, R.M. Yatsyk, and E.M. Bakalenko, who substantiated the expediency of the reserve's creation, Y.I. Dutchyn, T.M. Oleksiv, and V.O.Oleksiv, V.O. Saviuk, G.O. Masliak, M.M. Prykhodko, M.B. Shpilchak and K.O. Turchak, who approved and contributed to its approval and establishment.
The Gorgany NatureReserve is primarily a reference area of nature preserved in its natural, unaltered form.
TheGorgany Nature Reserve is a nature conservation and research institution. Its main tasks are to protect and preserve natural complexes and objects, conduct scientific research and observation of the state of the environment, develop environmental recommendations, and disseminate environmental knowledge.
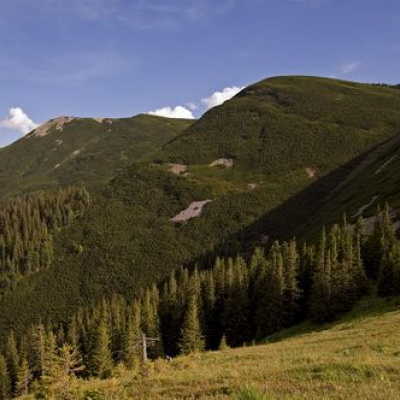
The Gorgany Mountains occupy the central part of the Ukrainian Carpathians and are difficult to access due to very steep slopes and rocky placers. The reserve covers mountain slopes from 710 meters above sea level up to the ridges: Dovbushanka (1754.6 m above sea level), Vedmezhyk (1736 m), Polensky (1693.6 m), Pikun (1651 m), Koziy Gorgan (1616), Skalky Verkhni (1596.8 m), Babyn Pogar (1478 m), Skalky Nyzhni (1300 m), which stretch from northwest to southeast. They are characterized by steep asymmetrical slopes and sharp mountain crests; on the tops there are stone scree (locally called "Gorgany"). The reserve is dominated by forest vegetation (85.5% of the area). It is dominated by coniferous forests (4524.8 hectares), with broadleaf forests occupying approximately 1% of the forested area (45.7 hectares). The largest areas of the reserve are occupied by forests with a predominance of spruce (Picea abies) - 89.1%. The stands of mountain pine (Pinus mugo) - 7.3%, European cedar (Pinus sembra) - 1.8%, white fir (Abies alba), forest beech (Fagus sylvatica) and other species cover 1.8% of the forested area. The most widespread are spruce-fir (2377.9 hectares) and beech-fir-spruce (1196.3 hectares) stands.
The virgin forests in the Gorgany are better preserved than anywhere else in the Ukrainian Carpathians, and they are characterized by high resilience and stability. Virgin forests are fairly large forest ecosystems (communities) that have arisen and are developing naturally under the influence of natural elements and phenomena and have gone through a full cycle of development without any human intervention, whose habitat, species, age and spatial structure have been and are determined exclusively by environmental factors. The largest trees of spruce, beech and fir in the virgin forests reach a height of 53 m and a diameter of more than 160 cm, and cedar - 34 m and a diameter of 108 cm.
The vegetation gives the mountains a magical beauty. In spring they are pale emerald, in summer they are densely green, in autumn they are all shades of gold, and in winter they are gray-brown. The reserve is home to 459 species of higher vascular plants belonging to 5 divisions, 79 families, and 270 genera. A significant part of the species are rare, endemic (distributed in a small area) and relict (remnants of flora of past geological times). Thirty-four species of vascular plants listed in the Red Data Book of Ukraine (more than 20% of the total number of such plants growing in the Ukrainian Carpathians) were found in the protected area. In total, the Reserve's rare flora includes 67 species of vascular plants. This is 17.1% of the rare component of the Ukrainian Carpathians and 63% of the Gorgan region. The rarest of them are: male cuckoo's mallow (Orchis mascula) and helmeted cuckoo's mallow (Orchis militaris), ovoid cuckoo's tears (Listera ovata), green tongue (Coeloglossum viride), and reviving lunaria (Lunaria rediviva). Among the relics are the following: multifidum botrychium, common ostrich feather (Matteuccia struthiopteris), spiky blechnum (Blechnum spicant), common lamb's-ear (Huperzia selago), and common wolf's-eye (Daphne mezereum). Among the endemic species are the round-leaved cornflower (Leucanthemum rotundifolia), Carpathian tozzia (Tozzia carpatica), Marmarosa cornflowers (Centauera marmarosiensis) and Carpathian cornflowers (Centaurea carpatica), Carpathian carnation (Dianthus carpaticus), rejected violet (Viola declinata) and others.
In the reserve and in the adjacent territories, 174 species of vertebrate fauna have been recorded (birds Aves - 104, mammals Mammalia - 42, fish Pisces - 12, amphibians Amphibia - 9, reptiles Reptilia - 6, round-headed hyperoartia - 1). Of these, 33 species are listed in the Red Data Book of Ukraine, 91 species are under special protection under the Bern Convention, 1 species with an unsatisfactory state of conservation is protected by the Bonn Convention, 7 species are listed in the IUCN Red List, and 4 species are listed in the European Red List.
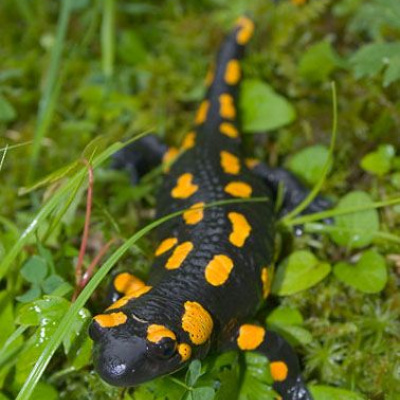
Here, the habitats of the most vulnerable large mammals have been preserved with little change: red deer (Cervus elaphus), chamois (Capreolus capreolus), brown bear (Ursus arctor), wolf (Canis lupus), etc. The fauna of invertebrates (1077 species) is also diverse in the reserve, among which insects are the most numerous group. The fauna is closely related to the high-altitude vegetation zones, so a significant part of it is characterized by species typical of coniferous forests. The following species of the taiga complex can be found here: Lynx lynx, Strix uralensis, Dryocopus martius, Pyrrhula pyrrhula, as well as species typical of broadleaf forests: Turdus merula, Dendrocopos medius, Dendrocopos leucotos, Picus canus, Ficedulla albicollis, Coccothraustes coccothraustes, Columba oenas, Muscardinus avellanarius, Felis silvestris, Salamandra salamandra. Only the snow mole (Chionomys nivalis) and the alpine fescue (Prunella collaris) are ecologically connected with the subalpine zone.
Although it is not allowed to visit the territory of the Gorgany Nature Reserve for tourist purposes, it is still possible to see the picturesque landscapes and nature protection objects. For this purpose, there is a scientific and educational trail on the territory of the reserve, and several tourist routes are marked outside the protected area.
From Yaremche, or the village of Dora, you can go to Mount Sinyachka (1402 m), Yaremche - Mount Yavirnyk-Horgan (1467 m).
In clear weather, Synyachka offers some of the most picturesque views in the Ukrainian Carpathians. In the south, above the longitudinal ridge of Yavirnyk, you can see the main peaks of the Eastern Gorgan Mountains: Khomyak (1544m), Vedmezhyk (1,736m), Pikun (1,651m), Polensky (1,693.3m), Koziya-Horgan (1,617m). Such landscapes are also visible from the Yavirnyk-Gorgana mountain.
Possible routes:
- м. Nadvirna - Pasichna village - Mount Verkhni Pody (1000 m) - Mount Pidsmerechek (1252 m) - Mount Synyachka (1402 m).
- м. Nadvirna - Pasichna village - Maidan mountain range - Zelena village - Zelenytsia and Chernyk villages - Berdulets State Reserve - Chernyk, Sadky and Novobudova mountain ranges of the Gorgany Nature Reserve - Mount Berezovachka (1500 m).
Mount Verkhni Podi offers magnificent views. In the west, you can see the peaks of the watershed ridge: Gropa (1758 m), Durnia (1709 m), Taupysh (1450 m), Syvula and Vysoka. The entire eastern part of the Gorgany Reserve is visible from Mount Pidsmerichok.
On the Bukhtivets tributary, which flows through the Maidan tract, there is a beautiful waterfall where you can have a good rest. And on Mount Berezovachka, there is a historical monument of the UPA's liberation struggle, the Thunder Bunker.
Accommodation around Gorgany Nature Reserve, Nadvirna:
Які маршрути проходять повз Gorgany Nature Reserve, Nadvirna?
Пропонуємо пройти такі туристичні (пішохідні) маршрути через/біля Gorgany Nature Reserve, Nadvirna: прис. Дора - скеля Білий Камінь - г. Синячка - пол. Щівка - прис. Дора, с. Дора, через г. Синячка, хр. Чорногориця до м. Яремче, с. Дора, через г. Синячка, пол. Чорногориця до м. Яремче, с. Дора, через г. Синячка, пер. Пересліп, пол. Туршугувата, хр. Явірник до м. Яремче, с. Дора, через г. Синячка, пер. Пересліп до м. Яремче, с. Дора, через г. Білий Камінь, г. Синячка до с. Дора
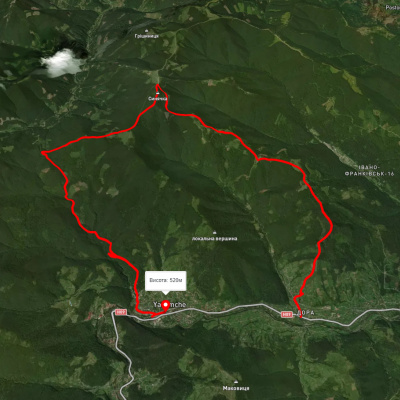
прис. Дора - скеля Білий Камінь - г. Синячка - пол. Щівка - прис. Дора
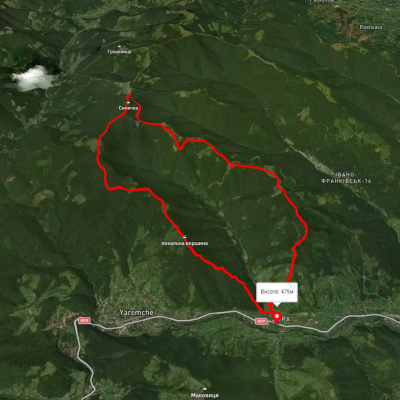
с. Дора, через г. Синячка, хр. Чорногориця до м. Яремче
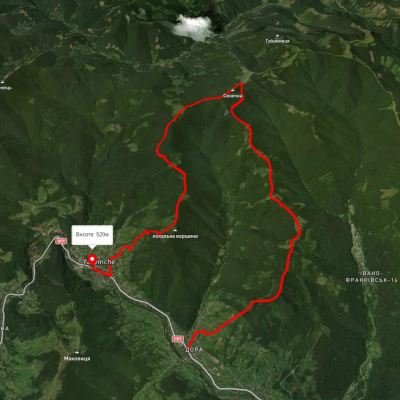
с. Дора, через г. Синячка, пол. Чорногориця до м. Яремче
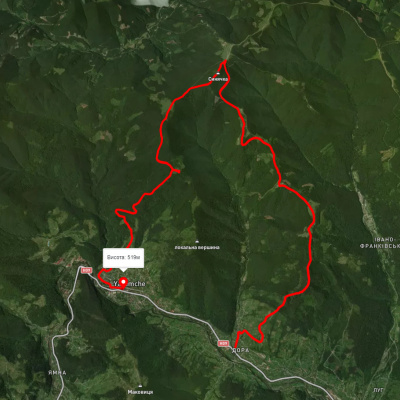
с. Дора, через г. Синячка, пер. Пересліп, пол. Туршугувата, хр. Явірник до м. Яремче